The Zones are Changing: A Guide to USDA Hardiness Zones
For avid gardeners and plant enthusiasts, understanding the USDA Hardiness Zones is akin to unlocking the secret code to successful gardening. These zones serve as a valuable tool, helping individuals choose plants that are best suited to their local climate and ensuring a thriving garden year-round. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of USDA Hardiness Zones, exploring what they are, why they matter, and how they can be a gardener's best ally … but there’s a catch. The zones are changing!
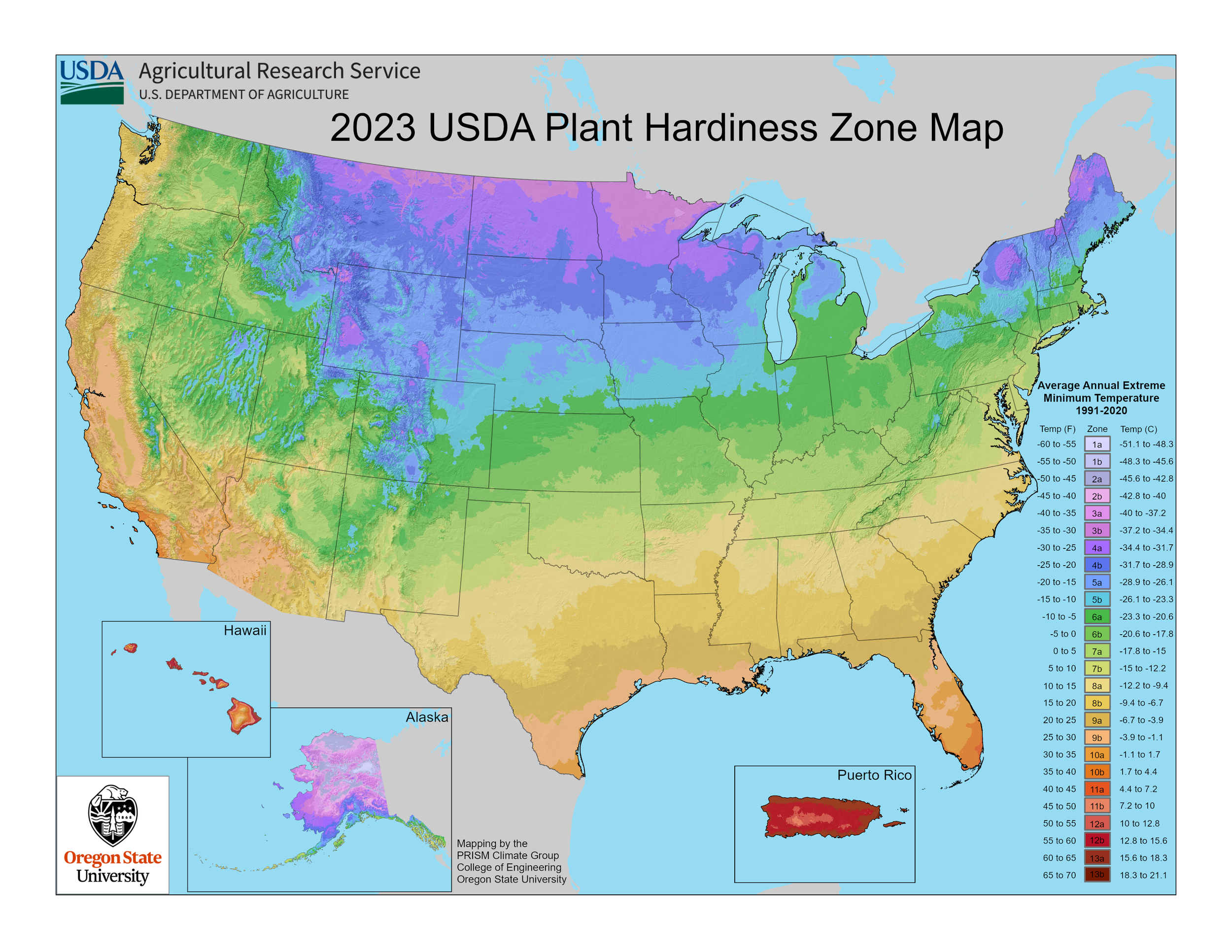
Thanks to warming average temperatures over the last few decades, the zone map was updated in the fall of 2023. The USDA uses average temperatures for the last 30 years to determine whether the maps needs significant updates or not. The last time the map was updated was in 2012 and 1990 before that. The new map is generally about one quarter-zone warmer than reported in the 2012 map throughout much of the United States, because of a more recent averaging period (1976-2005 vs. 1991-2020).
What Are USDA Hardiness Zones?
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Hardiness Zones are a comprehensive map that divides North America into specific geographic regions based on the average annual minimum winter temperature. Each zone is assigned a numerical value, ranging from Zone 1 (coldest) to Zone 13 (warmest), with each zone representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference. To further tailor zones to gardening needs, these zones are divided in 26 half zones.
Why Do USDA Hardiness Zones Matter?
Image via pxHere - CC0 Public Domain
1. Plant Suitability:
One of the primary purposes of the Hardiness Zones is to guide gardeners in selecting plants that are well-adapted to their local climate. Each plant species has a temperature range in which it thrives, and by choosing plants within the appropriate zone, gardeners increase the likelihood of success.
2. Winter Survival:
The zones are particularly crucial in gauging a plant's ability to withstand low winter temperatures. Knowing the average minimum winter temperature in your region helps you select plants that can endure the local winter conditions without succumbing to frost or freezing.
3. Growth and Bloom Timing:
The USDA Hardiness Zones also provide insight into the growing season length. Plants that are suited to a specific zone will typically emerge from dormancy and begin their growth cycle at the appropriate time, ensuring a harmonious and well-timed blooming period.
How to Determine Your USDA Hardiness Zone:
1. Online Tools:
Numerous online resources, including the USDA's own Plant Hardiness Zone Map, allow you to input your zip code or location to find your corresponding hardiness zone.
2. Gardening Guides:
Gardening catalogs, plant labels, and seed packets often include information about the suitable hardiness zones for the plants they offer. Always check this information before making a purchase. For example, the plant might say it is suitable for Zones 6-10 or it might just list one zone like Zone 5. In this case you would assume that zone 5 and warmer (5-13) is suitable.
3. Consult Local Experts:
Local nurseries, agricultural extension offices, and gardening clubs are excellent resources for gaining insights into the specific challenges and opportunities presented by your region's hardiness zone. Here at Bob’s we select plants that are suitable for our local hardiness zones (6-7). Knowing your zone really comes in handing when buying seeds or plants online or from a catalog.
Photo by John Morgan
Adapting to Your Zone:
While the USDA Hardiness Zones provide valuable guidance, they are not absolute rules. Microclimates, elevation, and other local factors can influence temperature variations. Gardeners should use the zones as a starting point and observe how specific plants respond to their individual garden conditions.
In our region, the Ohio River creates a significant microclimate in the fall. It’s waters, warmed by the heat of summer, help keep gardens in the river valley warmer than gardens just a few miles away. Often thick blankets of fall fog will protect gardens next to the river from the first frosts of autumn.
In the intricate tapestry of gardening, understanding and embracing your USDA Hardiness Zone is a key element for success. It's a tool that empowers you to make informed decisions, select the right plants, and cultivate a garden that not only survives but thrives in harmony with the unique climate of your region. So, whether you're a seasoned gardener or a beginner with a green thumb, let the Hardiness Zones be your guide as you embark on a journey of blooming beauty and verdant vitality.
2023 USDA Zone Map via USDA